排序是我们的日常开发中经常会遇到的需求,例如,在商品的列表页面,我们可以根据各种维度(销量、价格、人气等)对商品的展示顺序进行改变。
所以,对各个排序的性能的了解也是基础且重要的。我们先对排序这一块进行一个整体的把握。
冒泡排序
选择排序
插入排序
希尔排序
堆排序
归并排序
快速排序
关于排序的具体过程,本文没有利用图示来具体说明,但是在代码中对每一步执行加上了一些 log,有兴趣的可以复制代码到自己的 Playgroud 中运行查看。
冒泡排序 基本思想
两两比较相邻记录,如果反序则交换,直到没有反序的记录为止。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 func bubbleSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items for i in 0..<arr.count { print("第\(i + 1)轮冒泡:") var j = arr.count - 1 while j > i { if arr[j-1] > arr[j] { print("\(arr[j-1]) > \(arr[j]): 进行交换") arr.swapAt(j-1, j) } else { print("\(arr[j-1]) <= \(arr[j]): 不进行交换") } j -= 1 } print("第\(i + 1)轮冒泡结束") print("当前结果为:\n\(arr)\n") } return arr }
根据上面的实现过程,可以发现如果数组是类似于 [2, 1, 3, 4, 5] 的话,两次冒泡之后,数组就已经调整为 [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]。此时,再执行后面的循环其实是多余了,所以我们在发现冒泡循环没有进行交换的话,说明排序就已经完成了。下面我们可以将代码优化一下:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 func bubbleSort_v2(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items var flag = true for i in 0..<arr.count { print("第\(i + 1)轮冒泡:") if !flag { return [] } flag = false var j = arr.count - 1 while j > i { if arr[j-1] > arr[j] { print("\(arr[j-1]) > \(arr[j]): 进行交换") arr.swapAt(j-1, j) flag = true } else { print("\(arr[j-1]) <= \(arr[j]): 不进行交换") } j -= 1 } print("第\(i + 1)轮冒泡结束") print("当前结果为:\n\(arr)\n") } return arr }
选择排序 基本思想
每一次从待排序的数据元素中选择最小(或最大)的一个元素放在已排好序列的末尾,直到所有元素排完为止。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 func selectSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items for i in 0..<arr.count { print("第\(i+1)轮选择,x选择下标的范围为\(i)----\(arr.count)") var j = i + 1 var minValue = arr[i] var minIndex = i // 寻找无序部分中最小值 while j < arr.count { if minValue > arr[j] { minValue = arr[j] minIndex = j } j = j + 1 } print("在后半部分乱序数列中,最小值为:\(minValue),下标为:\(minIndex)") // 与无序表中的第一个值交换,让其成为有序表中的最后一个值 if minIndex != i { arr.swapAt(minIndex, i) } print("本轮结果为:\(arr)\n") } return arr }
插入排序 基本思想
每一步将一个待排序的记录,插入到前面已经排好序的有序序列中去,直到插完所有元素为止,最终可以得到一个有序表。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 func insertSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items for i in 0..<arr.count { print("第\(i)轮插入:") print("要选择插入的值为:\(arr[i])") var j = i while j > 0 { if arr[j] < arr[j-1] { arr.swapAt(j, j-1) j -= 1 } else { break } } print("插入的位置:\(j)") print("本轮插入完毕,插入结果为:\n\(arr)\n") } return arr }
希尔排序 基本思想
其实希尔排序是插入排序的升级版,希尔排序根据其排序的特点又叫做缩小增量排序。希尔排序的大体步骤就是先将无序序列按照一定的步长(增量)分为几组,分别将这几组中的数据通过插入排序的方式将其进行排序。然后缩小步长(增量)分组,然后将组内的数据再次进行排序。直到增量为 1 位置。经过上述这些步骤,我们的序列就是有序的了。其实上述的插入排序就是增量为 1 的希尔排序。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 func hillSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items var step: Int = arr.count / 2 while step > 0 { print("步长为\(step)的插入排序开始:") for i in 0..<arr.count { var j = i + step while j >= step && j < arr.count { if arr[j] < arr[j-step] { arr.swapAt(j, j-step) j = j - step } else { break } } } print("步长为\(step)的插入排序结束") print("本轮排序结果为:\(arr)\n") step = step / 2 // 缩小步长 } return arr }
堆排序 准备知识
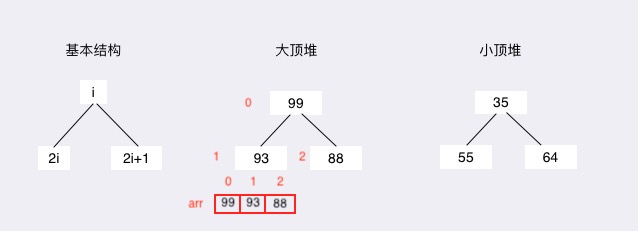
堆 是具有以下性质的完全二叉树:每个结点的值都大于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为大顶堆;或者每个结点的值都小于或等于其左右孩子结点的值,称为小顶堆。
我们对堆中的结点按层进行编号,将这种逻辑结构映射到数组中就是下面这个样子。
大顶堆: arr[i] >= arr[2i+1] && arr[i] >= arr[2i+2]
小顶堆: arr[i] <= arr[2i+1] && arr[i] <= arr[2i+2]
基本思想
将待排序序列构造成一个大顶堆,此时,整个序列的最大值就是堆顶的根节点。将其与末尾元素进行交换,此时末尾就为最大值。然后将剩余 n-1 个元素重新构造成一个堆,这样会得到 n 个元素的次小值。如此反复执行,便能得到一个有序序列了。
基本步骤
将无序序列构建成一个堆,根据升序降序需求选择大顶堆或小顶堆。
将堆顶元素与末尾元素交换,将最大元素”沉”到数组末端。
重新调整结构,使其满足堆定义,然后继续交换堆顶元素与当前末尾元素,反复执行调整及交换步骤,直到整个序列有序。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 // 构建小顶堆的层次遍历序列 func heapCreate(items: inout Array<Int>) { var i = items.count while i > 0 { heapAdjast(items: &items, startIndex: i - 1, endIndex: items.count) i -= 1 } } // 对小顶堆j的局部进行调整, 使其该节点的所有父类符合小顶堆的特点 func heapAdjast(items: inout Array<Int>, startIndex: Int, endIndex: Int) { let temp = items[startIndex] var fatherIndex = startIndex + 1 //父节点下标 var maxChildIndex = 2 * fatherIndex //左孩子下标 while maxChildIndex <= endIndex { if maxChildIndex < endIndex && items[maxChildIndex-1] < items[maxChildIndex] { maxChildIndex = maxChildIndex + 1 } if temp < items[maxChildIndex-1] { items[fatherIndex-1] = items[maxChildIndex-1] } else { break } fatherIndex = maxChildIndex maxChildIndex = 2 * fatherIndex } items[fatherIndex-1] = temp } func heapSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { var arr = items var endIndex = arr.count - 1 print("原始堆") print(arr) // 创建小顶堆,其实就是讲arr转换成小顶堆层次的遍历结果 heapCreate(items: &arr) print(arr) print("堆排序开始") while endIndex > 0 { // 将小顶堆的定点与小顶堆的最后一个值进行交换 arr.swapAt(endIndex, 0) endIndex -= 1 // 缩小小顶堆的范围 // 对交换后的小顶堆进行调整,使其重新成为小顶堆 print("重新调整") heapAdjast(items: &arr, startIndex: 0, endIndex: endIndex + 1) print("调整后的结果如下") print(arr) } return arr }
归并排序 基本思想
归并排序是利用归并的思想实现的排序方法,该算法采用经典的分治策略。
将需要排序的数组分解为一个个单独的子元素,两两比较后将其合并为一个有序数组,不断重复比较及合并的过程,直至合并之后的有序数组的元素数量与原数组相同时,则排序结束。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 // 合并两个数组 func mergeArray(firstList: Array<Int>, secondList: Array<Int>) -> Array<Int> { var resultList: Array<Int> = [] var firstIndex = 0 var secondIndex = 0 // 拿出两数组第一个元素,比较之后取小的插入新数组 while firstIndex < firstList.count && secondIndex < secondList.count { if firstList[firstIndex] < secondList[secondIndex] { resultList.append(firstList[firstIndex]) firstIndex += 1 } else { resultList.append(secondList[secondIndex]) secondIndex += 1 } } // 将第一个数组剩下的元素插入新数组 while firstIndex < firstList.count { resultList.append(firstList[firstIndex]) firstIndex += 1 } // 将第二个数组剩下的元素插入新数组 while secondIndex < secondList.count { resultList.append(secondList[secondIndex]) secondIndex += 1 } return resultList } func mergeSort(_ items: [Int]) -> [Int] { let arr = items // 将数组中的每一个元素放入一个数组中 var tempArray: Array<Array<Int>> = [] for item in arr { var subArray: Array<Int> = [] subArray.append(item) tempArray.append(subArray) } // 对这个数组中的数组进行合并,直到合并完毕为止 while tempArray.count != 1 { print(tempArray) var i = 0 while i < tempArray.count - 1 { print("将\(tempArray[i])与\(tempArray[i+1])合并") tempArray[i] = mergeArray(firstList: tempArray[i], secondList: tempArray[i+1]) print("合并结果为:\(tempArray[i])\n") tempArray.remove(at: i + 1) i = i + 1 } } return tempArray.first! }
快速排序 基本思想
快速排序(Quick Sort)使用分治法策略。
选择一个基准数,通过一趟排序将要排序的数据分割成独立的两部分;其中一部分的所有数据都比另外一部分的所有数据都要小。然后,再按此方法对这两部分数据分别进行快速排序,整个排序过程可以递归进行,以此达到整个数据变成有序序列。
快速排序流程:
从数列中挑出一个基准值。
将所有比基准值小的摆放在基准前面,所有比基准值大的摆在基准的后面(相同的数可以到任一边);在这个分区退出之后,该基准就处于数列的中间位置。
递归地把“基准值前面的子数列”和“基准值后面的子数列”进行排序。
代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 /// 将数组以第一个值为准分为两部分,前半部分比该值要小,后半部分比该值要大 /// /// - parameter list: 要二分的数组 /// - parameter low: 数组的下界 /// - parameter high: 数组的上界 /// /// - return: 分界点 func partition(list: inout Array<Int>, low: Int, high: Int) -> Int { var low = low var high = high let temp = list[low] while low < high { while low < high && list[high] >= temp { high -= 1 } list[low] = list[high] while low < high && list[low] <= temp { low += 1 } list[high] = list[low] print("====low==\(low)======high==\(high)") } list[low] = temp print("=====temp==\(temp)") print(list) return low } /// 快速排序 /// /// - parameter list: 要排序的数组 /// - parameter low: 数组的下界 /// - parameter high: 数组的上界 func quickSortHelper(list: inout Array<Int>, low: Int, high: Int) { if low < high { let mid = partition(list: &list, low: low, high: high) quickSortHelper(list: &list, low: low, high: mid - 1) quickSortHelper(list: &list, low: mid + 1, high: high) } } func quickSort(_ items: Array<Int>) -> Array<Int> { var list = items quickSortHelper(list: &list, low: 0, high: list.count - 1) print("快速排序结束") return list }
Swift排序用法 在Swift源代码中,sort 函数采用的是一种内审算法(IntroSort)。它由堆排序、插入排序、快速排序三种算法构成,依据输入的深度相应选择最佳的算法来完成。
1 2 3 4 5 // 以升序排列为例,array 数组可改变 array.sort // 以降序排列为例,array 数组不可改变 newArray = array.sorted(by: >)
总结
排序方法
时间复杂度
辅助空间
冒泡排序
O(n²)
O(1)
选择排序
O(n²)
O(1)
插入排序
O(n²)
O(1)
希尔排序
与增量选取策略有关
O(1)
堆排序
O(nlogn)
O(1)
归并排序
O(nlogn)
O(n)
快速排序
O(nlogn)
O(logn)-O(n)